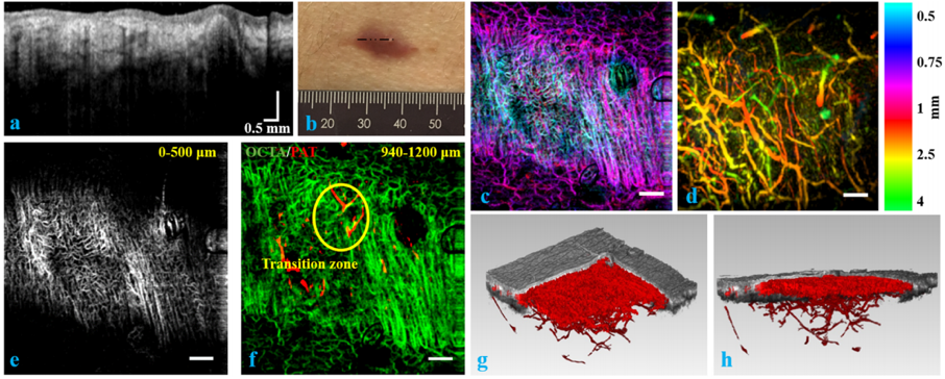
Bimodal Photoacoustic / Optical Coherence Tomography (PAT/OCT) *
Photoacoustic Imaging (PAI) is a hybrid optical imaging modality which detects laser pulse induced ultrasonic waves. It can resolve the absorbers located in turbid media. Since the contrast is purely based on optical absorption, the imaging depth of PAI goes beyond the optical mean free path. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), on the other hand, uses scattering contrast. Based on low coherence interferometry, OCT is superb in resolving layered structures. An extension of OCT, namely OCT angiography (OCTA), can produce contrast based on speckle or phase variance. Combining OCT and PAI provides complementary tissue optical absorption, scattering information, and deep tissue structures. An imaging area of 15 mm × 15 mm can be achieved. This non-invasive, in vivo technology can be applied in both preclinical and clinical applications.